First 5 cell lines in Allen Cell Collection empower the cell science community to explore the dynamic organization of the cell and to better understand health and disease
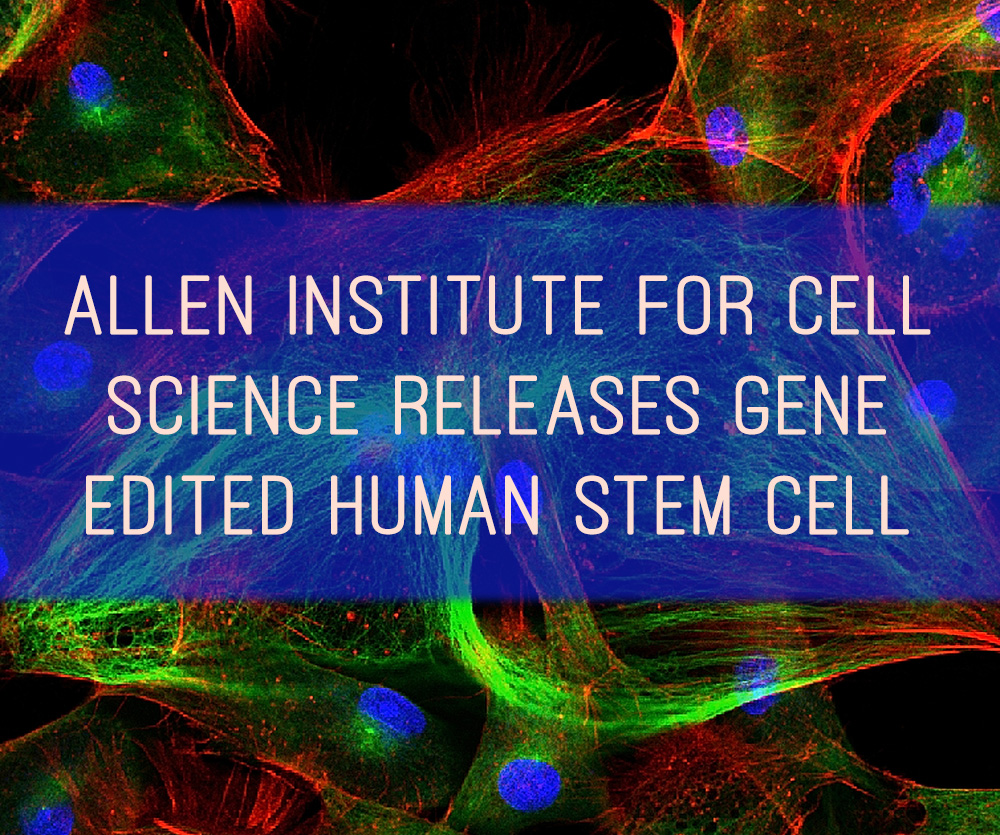
 November 30, 2016 — The Allen Institute for Cell Science has released the Allen Cell Collection: the first publicly available collection of gene edited, fluorescently tagged human induced pluripotent stem cells that target key cellular structures with unprecedented clarity. Distributed through the Coriell Institute for Medical Research, these powerful tools are a crucial first step toward visualizing the dynamic organization of cells to better understand what makes human cells healthy and what goes wrong in disease.
November 30, 2016 — The Allen Institute for Cell Science has released the Allen Cell Collection: the first publicly available collection of gene edited, fluorescently tagged human induced pluripotent stem cells that target key cellular structures with unprecedented clarity. Distributed through the Coriell Institute for Medical Research, these powerful tools are a crucial first step toward visualizing the dynamic organization of cells to better understand what makes human cells healthy and what goes wrong in disease.
“Each of our cells—the fundamental units of life—are like a city, with people and resources that move around and factories that generate those resources and carry out important functions,” says Rick Horwitz, Ph.D., Executive Director of the Allen Institute for Cell Science. “With these cell lines, we aim to give the cell science community a kind of live traffic map to see when and where the parts of the cell are with the clarity and consistency they need to make progress toward understanding human health and tackling disease.
Scientists at the Allen Institute for Cell Science used CRISPR/Cas9 technology to insert fluorescent tags for major cellular structures into human induced pluripotent stem cells.
Unlike typical methods which flood the cell with fluorescent protein, these highly precise tags show exactly when and where the structures are at various stages in the cell’s lifecycle.
“By lowering the barrier to entry for cell biologists wishing to work on iPS cells, the availability of these lines will usher in a new era in cell biology,” says Anthony Hyman, Ph.D., Director and Group Leader at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics.
This first collection of five cell lines targets a set of major cellular structures that help to orient the cell. These include the nucleus (tagged by the protein lamin B1), mitochondria (Tom20), microtubules (alpha-tubulin), cell-to-cell junctions (desmoplakin) and adhesion (paxillin). Subsequent collections will be released throughout 2017.
“This kind of precise fluorescent tagging of structures in human stem cells is valuable for a variety of reasons, not least of which is that the pluripotent stem cells can be turned into a large number of cell types, like heart, brain or skin,” says Ruwanthi Gunawardane, Ph.D., Director of Stem Cells and Gene Editing at the Allen Institute for Cell Science. “Our cells are healthy and as close to normal human cells as we can study in the lab, making these cell lines a powerful platform to identify the functions of genes, screen drugs, determine differentiation state and much more.”
“With these tagged cell lines, we get to ‘spy’ on the organization of healthy, normal human cells in a way that scientists never could before,” says Susanne Rafelski, Ph.D., Director of Assay Development at the Allen Institute for Cell Science. “The images and movies we can generate from these lines show the cell’s major structures with astonishing clarity and empower a broad, multi-structure view of how cells change as they execute their various activities and turn into different kinds of cells.”
The cell lines will be available for scientists around the world to use not just to understand the fundamentals of the cell, but also to investigate disease. Key mutations can be introduced to the cells in order to study how disease progresses in a dish, with broad potential impacts on the fields of biomedical science and personalized medicine.
For more information about the Allen Cell Collection at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research, visit catalog.coriell.org/AllenCellCollection.
About the Allen Institute for Cell Science
The Allen Institute for Cell Science is a division of the Allen Institute (alleninstitute.org), an independent, 501(c)(3) nonprofit medical research organization, and is a research organization dedicated to understanding and modeling cells: the fundamental units of life. By integrating technologies, approaches, models and data into a common standardized framework, the Allen Institute for Cell Science is creating dynamic, visual models of how genetic information is transformed into cellular behavior, and how the molecules and organelles within each cell interact and function as systems.
These predictive models will enable the cell science community to better understand the role of cells in both health and disease. The Allen Institute for Cell Science was launched in 2014 with a contribution from founder and philanthropist Paul G. Allen. The data, tools and models from the Allen Institute for Cell Science will be publicly available online.
About the Coriell Institute for Medical Research
 Coriell Institute for Medical Research is recognized as one of the world’s leading biobanks, distributing biological samples and offering research and biobanking services to scientists around the globe. A pioneer in genomics, Coriell is examining the utility of genetic information in clinical care through the Coriell Personalized Medicine Collaborative (CPMC) research study. The Institute is also unlocking the promise of induced pluripotent stem cells and their role in disease research and drug discovery.
Coriell Institute for Medical Research is recognized as one of the world’s leading biobanks, distributing biological samples and offering research and biobanking services to scientists around the globe. A pioneer in genomics, Coriell is examining the utility of genetic information in clinical care through the Coriell Personalized Medicine Collaborative (CPMC) research study. The Institute is also unlocking the promise of induced pluripotent stem cells and their role in disease research and drug discovery.
Source: Allen Institute for Cell Science
Download the full press release from the Allen Institute for Cell Science.


















Tell Us What You Think!