|
|
In addition to the use of stem cells for the treatment of cancer and other chronic diseases, stem cell treatments for hips are being now showing great promise.
Throughout time and across the world, people have aged into delicacy, and ultimately, decline. While death is a natural part of the human condition – the end any organism can expect eventually – it sometimes comes sooner than it needs. Even when it doesn’t, decline makes life more difficult and the body less sound. This hard fact has made the possibility of stem cell treatments for hips and other parts of the body appealing.
Stem cell procedures of a wide variety have gained traction in recent years. Scientists have lined up many diseases in their sights: cancer, neurological disorders, tooth decay, eye conditions, and more. Regenerative medicine enables the body to heal damaged or aged parts that would otherwise never recover.
Which leads us back to hips: Where do degenerative conditions come from? How do degenerative diseases affect the hips? Who suffers from them? How can stem cell treatments aid in the healing/improvement of hips? What are the different types of stem cell treatments? What are the risks and benefits associated with them?
The answers to those questions form the foundational understanding needed for anyone considering a stem cell treatment to improve hip function. Read on to learn more.
Stem Cell Treatments For Hips | What You Need To Know
In this article:
- Why Do Bodily Structures Degenerate or Break Down?
- What Degenerative Diseases Affect the Hips?
- Stem Cell Treatments for Hips
- Stem Cell Sources
- Autologous vs Allogeneic Stem Cell Treatments
Why Do Bodily Structures Break Down?
It is normal for cells to die – in fact, humans lose about 300 million cells every minute. About 50,000 cells died and were replaced in the time it took to read the previous sentence. That gives a small window into the massive engine that is the human body. It constantly breaks down cells, recycles them and makes new ones.
This process is only healthy, however, insofar as cells get replaced by new ones in a timely fashion. A degenerative disease is one in which tissue deteriorates over time at a faster rate than the body can replenish it. That means that although cells are still dying and new cells are still getting made, the new replacements cannot keep up with the rate of die-off in existing tissues.
Degenerative diseases affect the body from top to bottom. Hypertension is a type of degenerative disease, as are Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Other tissues in the body can break down over time as well, including organ, bone and – most importantly for the purposes of this article – cartilage and other joint tissue.
What Degenerative Diseases Affect the Hips?

When the tissue that separates one bone from another at the joint begins to break down, that’s known as degenerative arthritis. It is also called age-related arthritis, degenerative joint disease, and osteoarthritis.
Arthritis, in general, is an inflammatory disease that affects the joints of the body. This causes painful swelling and immobility. Osteoarthritis has a range of associated ills. This includes making hip structures more brittle and prone to breakage to severely limiting mobility. Many people experience severe pain, ranging from a dull throb to a sharp and stabbing sensation. Obviously, that’s no way to live.
Slow breakdown over time isn’t the only cause of degenerative arthritis, either. A traumatic injury to the area can also cause issues with healthy tissue regeneration. For example, elderly people who fall and break their hip may not experience healthy regrowth of the area. Injury to the hip is an event that hospitalizes more than 300,000 people over the age of 65 every year.
Patients visit their doctors in droves every year to try and remedy joint pain and associated symptoms. Currently, physicians have limited means of treating these conditions – which usually worsen over time. The normal course of action includes anti-inflammatory drugs and occasionally a hip replacement procedure, both of which produce partial recovery at best.
Which leads to the question: What else can physicians do?
Stem Cell Treatments for Hips
Enter stem cell treatments for hips. With the current advances in stem cell growth and treatment, researchers have developed increasingly complex ways of addressing hip pain through stem cell therapy. This treatment usually involves first harvesting and then reinjecting cells from the patient’s own body. These injections contain both the stem cells and the compounds needed to stimulate their growth.
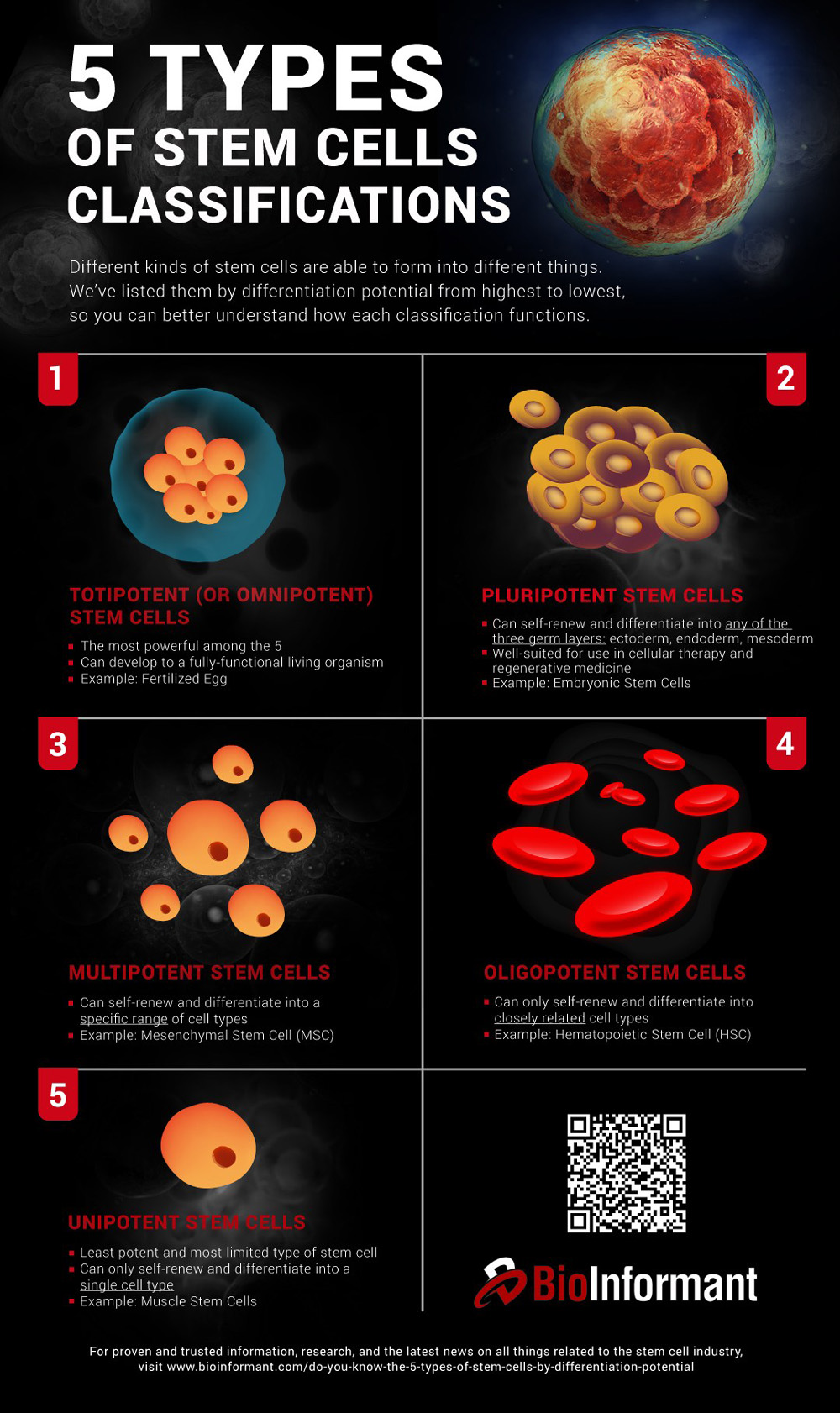
Some stem cell types are capable of being “blank cells” that can turn into a wide range of different cells. For instance, whereas a cartilage cell is no longer capable of regenerating itself through division, a stem cell can turn into the cartilage cell and thereby replace the degenerating tissue.
Other types of stem cells can exert therapeutic effects through cellular signals that they release. There are a number of proposed mechanisms as to how these effects might occur. These theories include paracrine signaling (a form of cell-to-cell communication) and the release of nano-sized vesicles called exosomes (small packages that act as cellular “mail”).
These mechanisms can lessen pain by reducing the inflammatory response or promoting a healthy immune response.
Stem Cell Sources
Researchers source of adult stem cells from a wide range of tissue types, including bone marrow, fat tissue, teeth, and several types of birth tissues, such as umbilical cord blood, cord tissue, and the placenta. In some cases, embryonic stem cells may be capable of providing good results, but the moral scuffles over their use make adult stem cells preferable.
In a recent study by Mardones, et al., titled Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis, researchers found that the injection of laboratory-expanded bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSC) to patients with cartilage defects of the hip was a safe and effective treatment in the “restoration of hip function and range of motion.” In addition to helping the hip joint repair itself, the stem cell procedure reduced inflammation and stiffness.
Autologous vs. Allogeneic Stem Cell Treatments
When a patient uses their own cells for the procedure, this is known as an autologous stem cell treatment. In this process, physicians harvest the stem cells directly from the patient themselves. These cells are then prepared in a lab. Using specialized procedures, these cells are inserted into the region of damage, where the cells may proliferate to repair the tissue or release cellular cues to stimulate repair. For example, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are known to exert therapeutic effects that can be anti-inflammatory, anti-scarring, and supportive of healthy immune system function.
However, it is not always possible to use one’s own cells. For instance, if a patient has cancer, the cells might carry the danger of reintroducing it when chemotherapy or radiation have otherwise wiped it out.
In that case, a patient might leverage the power of stem cell banks, whereby other people donate their stem cells for the greater public good. If their physician can find a match, then the patient can benefit from those cells. Stem cell donors can be family members, as well as donors from these public registries (cell banks).
Unfortunately, there are risks with this approach too. Stem cells from another person, called allogeneic stem cells, may initiate an immune response within the patient’s body. This is known as graft-versus-host disease, in which the graft (donated stem cells) attacks the host (person receiving them). Sometimes this can cause lifelong issues or even death.
Still, if the patient is able to locate a donor, this is often a risk they’re willing to take for particularly severe cases of hip degeneration of other painful, limiting diseases.
Seeking a Stem Cell Treatments for Hip Pain?
In alignment with what we believe, GIOSTAR’s goal is to offer cutting-edge, extensively researched stem cell therapy options designed to rejuvenate and improve a patient’s quality of life.
Click here to Schedule a Consultation or ask GIOSTAR a question about how stem cell therapy could help you.
What questions do you have about stem cell treatments for hips? Ask them in comments below.
Up Next: Stem Cell Treatments For Lungs

















Is this available for Canadians ?