|
|
MSCs are advantageous over other cell types for a variety of reasons. First, they avoid the ethical issues that surround embryonic stem cell research.
Second, repeated studies have found MSCs to be immuno-privileged, which make them an advantageous cell type for allogeneic transplantation. MSCs reduce both the risks of rejection and complications of transplantation.
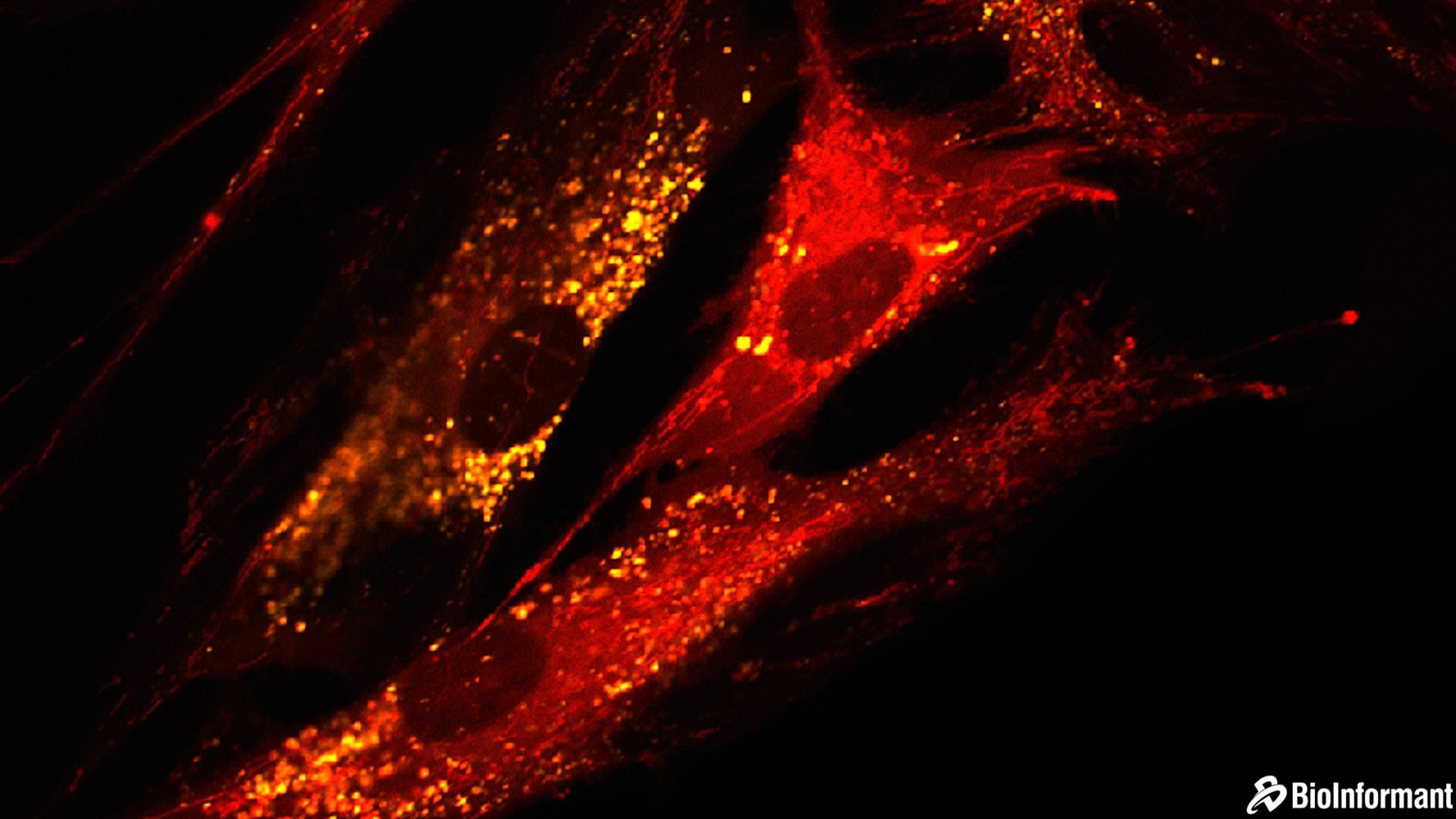
Third, there have been advances in the use of MSCs to regenerate human tissues, including cartilage, meniscus, tendons, and bone fractures, because MSCs can exert regenerative effects through honing to sites of damage, paracrine signaling, regulating the immune response, and positively affecting the microenvironment.
In combination, these traits make MSCs of intense therapeutic interest, because they represent a population of cells with the potential to treat a wide range of acute and degenerative diseases.
Top 10 MSC Benefits

1. Well-Characterized
MSCs are a well-characterized population of adult stem cells, with over 74,000 scientific articles published about them.
2. Non-Controversial
MSCs avoid the ethical issues of embryonic stem cells, as they can be derived from sources that include adult bone marrow and adipose tissue.
3. Diverse Differentiation Potential
MSCs can form a variety of cell types in the laboratory, including those of both intra- and extra-mesenchymal lineages. These cell types include fat (adipocytes), bone (osteoblasts), skin (dermal cells), nerve (neural cells), cartilage (chondrocytes), muscle (skeletal myocytes), tendons (tenocytes), marrow stroma, and ligaments.
4. Ease of Growth in Culture
Advanced knowledge exists for how to grow MSCs in culture, including protocols for isolation, expansion, and differentiation.
5. Flexible Propagation
MSCs can be grown and propagated in culture for extended periods, without losing differentiation potential.
6. Clinically Relevant Volumes
Unlike many other types of adult stem cells, MSCs can be acquired in the quantities required for clinical applications, as knowledge exists for how to culture the cell type in 3D bioreactors. It is understood that reduced oxygen conditions, along with available nutrients, assist MSC expansion under bioreactor conditions.[1]
7. Role as Regulatory Cells
MSCs synthesize and secrete a variety of macromolecules that are known regulators of hematopoietic and bone-resorbing cells.[2]
8. Delivery of Gene Products
MSCs can take up exogenous DNA and keep introduced genes, an attribute that may allow the use of the cells in the therapeutic delivery of molecules to target regions of the body.
9. Favorable Immune Status
MSCs lack the co-stimulatory molecules of the B7 family that are required to initiate an immune response.[3] This allows the administration of MSC preparations across MHC barriers without concern for immunological rejection or the need for immunosuppression, making MSCs a universal stem cells source.
10. Commercially Available Research Tools
Currently, dozens of research supply companies offer MSC-based products, making research tools for this cell type easily accessible.
Footnotes
[1] Godara P, et al. Mini-review: Design of bioreactors for mesenchymal stem cell tissue engineering. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 2008; 83: 408–420.
[2] Haynesworth S, Reuben D, Caplan A. Cell-based tissue engineering therapies: The influence of whole body physiology. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 1998; 33(1-2): 3-14.
[3] Tipnis S, Viswanathan C, Majumdar A. Immunosuppressive properties of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Role of B7-H1 and IDO. Immunology and Cell Biology 2010; 88: 795-806.



















Tell Us What You Think!